Managing Infrastructure with Secure Configurations#
Infrastructure management involves adjusting configuration settings for systems to reduce the risk of cyber attacks. Most workstations (e.g., desktop, laptops, tablets) should have capabilities limited to the job function they serve. Often, this is tied to the type of employee to which the workstation is issued, such as an admin or a poll worker. Sometimes, it’s about the use the workstation plays in the office. A similar rule applies to servers and other shared infrastructure.
In general, having a few configurations you use repeatedly is better than creating custom configurations for each system you allow in your environment. You should create these configurations or get them from a trusted source and carefully track any changes to them.
Implementing these configurations can be done manually or with automated tools.
Goals#
Properly configure workstation permissions (Level 1 maturity)
Leverage CIS Benchmarks for workstation and infrastructure configuration (Level 2 maturity)
Actions#
For Managing Infrastructure with Secure Configurations, the necessary actions vary by maturity as detailed below.
Level 1 Maturity#
Limit administrative access to machines that perform administrative functions.
If a machine has a short period of inactivity, force a lock screen or log out.
Employ the restrictions from the User Management best practice.
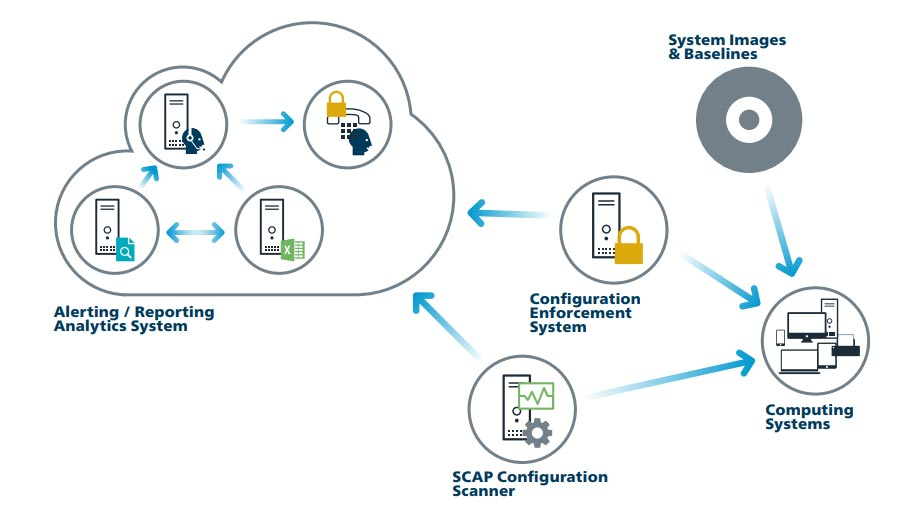
Work with IT staff or vendors to establish a process for configuring network infrastructure to ensure it is secure, consistent, and tracked.
Level 2 and Level 3 Maturities#
Organizations operating at a Level 2 or Level 3 maturity should take additional actions, including:
Leverage the CIS Benchmark on workstation management for your operating systems. This will allow for maintenance of a secure configuration process for network infrastructure.
Choose stricter security levels for systems with sensitive functions.
Consider CIS Benchmarks for servers, desktops, laptops, mobile devices, and software on systems.
Use the EMS Gateway Benchmark for machines that, through removable media, exchange data with the EMS.
Uninstall or disable unnecessary services on enterprise assets and software
Cost-Effective Tools#
Applocker: Free Microsoft® Windows tool to identify and restrict the software that is allowed to run.
Netwrix: Variety of free tools to identify information about administrative access on your systems.
OpenAudIT: Inventory applications and software on workstation servers and network devices.
CIS Benchmarks: Secure configurations for more than a hundred of the most common software applications.
Election Management System Gateway Benchmark: A CIS Benchmark to secure the machines that, through removable media, exchange data with the EMS.
Mapping to CIS Controls and Safeguards#
4.1: Establish and Maintain a Secure Configuration Process (Level 1 maturity)
4.2: Establish a Secure Configuration Process for Network Infrastructure (Level 1 maturity)
4.3: Configure Automatic Session Locking on Enterprise Assets (Level 1 maturity)
5.4: Restrict Administrator Privileges to Dedicated Administrator Accounts (Level 1 maturity)
4.2: Maintain a Secure Configuration Process for Network Infrastructure (Level 1 maturity)
12.8: Establish and Maintain Dedicated Computing Resources for All Administrative Work (Level 1 maturity)
4.8: Uninstall or Disable Unnecessary Services on Enterprise Assets and Software (Level 2 maturity)
Mapping to CIS Handbook Best Practices#
23, 27, 65, 68, 88